How EWOT Can Help You With Babesia Infection?
LISTEN TO THIS ARTICLE
Struggling with Babesia infection? Learn how Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT) can be an effective complementary treatment for fighting off Babesiosis
Key Points:
- Like Lyme Disease, Babesia infection (Babesiosis) is a tick-borne parasitic infection that targets and destroys Red Blood Cells.
- Babesia parasites put your body in a hypoxic (low oxygen) state by attacking the red blood cells, inhibiting Nitric Oxide release and reducing blood's capacity to carry oxygen to the tissues, leading to fatigue.
- Exercise with Oxygen Therapy combines exercise and the use of supplemental oxygen to increase oxygen delivery to cells, tissues, and organs.
- EWOT can help manage the symptoms of Babesia infection by increasing energy levels, reducing inflammation, improving exercise tolerance, and helping with detoxification.
You may be aware of Lyme disease, a tick-borne bacterial infection that, if left untreated, may cause fever, headache, skin rash, fatigue, arthritis, and irregular heartbeat. But have you heard of the babesia infection (babesiosis), a tick-borne parasitic illness that infects and destroys red blood cells? Over the past decade, there’s been a rise in the incidence of babesia infection in the United States, especially in the Northeast and Midwest regions.
Have you or someone you know ever had a Babesia infection, or are you currently dealing with an existing case? Or are you seeking ways to prevent the infection or lower the probability of reoccurrence? If so, did you know Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT) can help you deal with the symptoms of babesia infection and reduce the risk of recurrence?
Wondering how?
Read on to find out why and how EWOT can act as a complementary therapy for dealing with babesia infection.
Understanding Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT)
Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT), as the name suggests, is the practice of inhaling higher concentrations of oxygen while exercising. The synergistic combination of Exercise and Oxygen helps you increase your energy levels and reduce fatigue and inflammation by delivering a lot of oxygen to your cells, muscles, and organs. Can you believe you can reap these benefits with just 15 minutes of daily exercise, all from the comfort of your own home?
Understanding Babesia Infection and Its Symptoms
Babesiosis is a disease that affects your red blood cells and is caused by the Babesia parasite. A parasite is a living organism that lives on or inside another organism. The most common type of Babesia parasite infects humans in the U.S. is Babesia microti, transmitted by deer ticks (or black-legged ticks).
Babesiosis is generally asymptomatic. However, some individuals develop flu-like symptoms, such as fever, body aches, chills, fatigue, headache, loss of appetite, or sweating. As the babesia parasite damages your red blood cells, you may develop hemolytic anemia, a condition in which your red blood cells are destroyed more rapidly than they are made by bone marrow.
You might notice symptoms within 1-4 weeks of exposure, and they can linger for several weeks.
Babesia infection can be severe and potentially fatal, especially for the elderly, those with a weakened immune system, or those who have undergone splenectomy (surgical removal of the spleen).
The complications include:
- Jaundice
- Pale skin
- Shortness of breath
- Nausea & vomiting
- Stomach ache
- Stiffness on the neck
- Sudden changes in mood and emotions
How is Babesia Infection Transmitted?
An infected deer tick transmits Babesia parasites to humans through its bite. The parasites migrate from the tick’s gut to the host’s skin and eventually enter the bloodstream. After entering the bloodstream, the Babesia parasites multiply and destroy the red blood cells. The parasite can only be spread if a tick remains attached to a person for at least 36-48 hours. So, removing the ticks on time helps reduce the risk of infection. Many infections occur from the bite of nymphs, the tiny, difficult-to-spot ticks that are active during spring and summer.

Image credit: https://www.cdc.gov/babesiosis/spreads/index.html
On the left is an adult Ixodes Specularis (commonly known as black-legged or deer tick). On the right is a nymph, the young stage of the same species. The size difference highlights how small and difficult the nymph can be to detect.
Ticks can attach anywhere on the body, but they frequently hide in hard-to-see areas such as behind your knees, armpits, on your scalp, ears, belly button, and groin.

In some rare cases, babesia infection can be spread through infected blood products. Always remember early tick removal is your best defense against babesiosis.
How Does Babesia Parasite Affect Your Immune System?
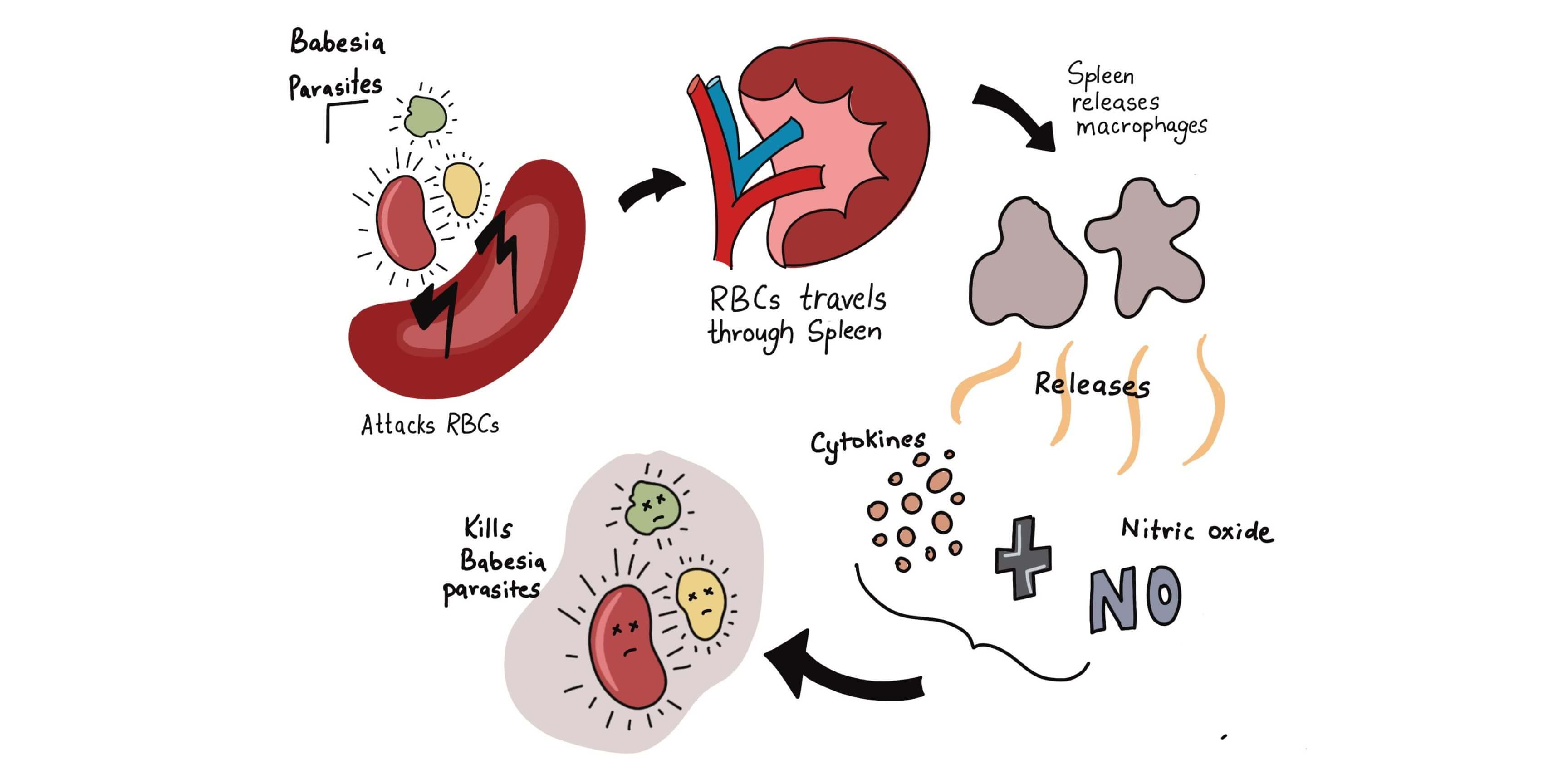
When the Babesia parasite attacks your body, the red blood cells carrying this parasite travel through your spleen. The spleen is an important part of your immune system that filters your blood. When the spleen detects these parasite-carrying red blood cells, it synthesizes macrophages, the white blood cells that help fight off the infections caused by the invaders. The macrophages release cytokines and nitric oxide to kill the pathogens.
However, the situation is different for immunocompromised individuals or those without a spleen, as they lack this defense mechanism and can’t activate the appropriate immune response. This makes them more susceptible to severe Babesia infections because their bodies can’t effectively fight off the parasite.
As the Babesia parasite targets red blood cells, it inhibits the release of nitric oxide, thereby reducing the ability of red blood cells to carry oxygen to the tissues. This makes your body hypoxic (deprived of oxygen) and fatigued. Low oxygen levels impair the mitochondria’s function and disrupt energy production, resulting in increased fatigue.
Well, now let’s take a look at how Nitric Oxide (NO) acts as the most multifaceted player in your body. NO is a jack-of-all-trades, playing a vital role in everything from immune system function and cardiovascular health to nerve transmission to wound healing and tissue repair, pathogen defense, vasodilation, and more.
Here are some ways to increase nitric oxide levels in the body:
- Supplements: Taking dietary supplements containing the amino acids L-Arginine and L-Citrulline
- Diet: Consuming foods rich in nitrate (beetroot, leafy green vegetables), which help your body convert nitrate to nitric oxide.
- Regular Exercise: Improves the function of endothelial cells which synthesize nitric oxide.
Remember, consistency is the key! You can adjust the frequency to fit your schedule and preferences. Find a routine that works for you and stick with it.
How Can EWOT Potentially Help You Manage Babesia Symptoms?
As mentioned before, Nitric Oxide helps regulate blood circulation, deliver oxygen, and transport nutrients, all of which are essential for physical performance. The increased blood flow indicates that your muscles receive more oxygen and nutrients, which in turn helps your body fight fatigue.
But did you know that exercise can increase the synthesis of nitric oxide? Yes, you read it right! Now, let me explain the connection between exercise and NO production. When you exercise, your blood gets flowing, and your endothelial health improves. Nitric oxide is produced by endothelial cells to improve the health of your blood vessels. Exercise has been shown to enhance endothelial vasodilation, offering significant benefits to healthy adults as well as individuals with hypertension and heart disease.
As the name suggests, nitric oxide consists of one oxygen atom and one nitrogen atom. So, oxygen is a key determinant of nitric oxide production. This is one of the reasons why Babesia infection creates oxygen deprivation and fatigue in your body. Research has shown that inhaling higher concentrations of oxygen, whether administered under high pressure (as in Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy) or normal pressure (as in Exercise with Oxygen Therapy), increases nitric acid synthesis.
The synergistic combination of oxygen and exercise can increase nitric oxide levels in your body. Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT) is the practice of inhaling higher concentrations of oxygen while exercising. Engaging in 15 minutes of EWOT daily is the best way to give your cells, tissues, and organs the oxygen they crave.
Here’s what EWOT can do for you to help manage the symptoms of Babesia infection:
Increases your energy levels: EWOT supplies your body with oxygen. This oxygen surge improves your mitochondrial function and increases the synthesis of ATP, your body’s energy molecule. The increase in energy helps your body fight off fatigue and accelerate recovery. For those with Babesiosis, we suggest you start gradually and listen to your body signals.
Improves your exercise tolerance: Engaging in physical activity can be challenging with Babesiosis due to fatigue and hypoxia. Exercising with oxygen can enhance exercise tolerance, making workouts less strenuous and increasing endurance.
Helps ease inflammation: Research has shown that nearly 25% of individuals with Babesiosis experience arthralgia (joint pain), and nearly 50% suffer from myalgia (nerve pain) and headache, all linked to chronic inflammation. The connection between inflammation and hypoxia is a two-way street. EWOT combats inflammation by increasing oxygen delivery to degenerate, hypoxic tissues, potentially reducing inflammation and promoting healing.
Aids in detoxification: Inhaling pure oxygen while exercising supports detoxification by helping your body remove excess carbon dioxide, reduce lactic acid buildup in muscles, and improve energy production and metabolism. When your cells function optimally, they become more efficient at carrying out detoxification processes.
Takeaway
In short, while research is still underway, Exercise with Oxygen Therapy (EWOT) can act as an effective adjunctive therapy for Babesia infection. By increasing oxygen levels and stimulating nitric oxide production, EWOT can help counteract the fatigue and hypoxia often experienced by persons with Babesia infection while also promoting healing and potentially creating a less favorable environment for the parasite.
FAQs
1. Can Babesia infection be prevented?
Yes, babesia infection and other tick-borne illnesses can be prevented by avoiding tick bites. You can follow these precautions to prevent tick bites and reduce the risk of infections:
- Wear light-colored, protective clothes.
- Use insect repellent that contains 10-30% DEET on exposed skin and clothes. Apply repellent to your hands first.
- Walk in the center of the trails to avoid contact with vegetation.
- Inspect yourself, kids, and pets every 2-3 hours.
- You can remove ticks using tweezers. If you find any ticks crawling on clothes, you can use masking tape to remove them. Don’t remove ticks by using petroleum jelly or home remedies, as this can increase the chances of developing a tick-borne illness.
- Safely dispose of ticks by placing them in soapy water/alcohol or flushing them down the toilet.
- Wash bite areas and hands with soap and water and apply an antiseptic.
- Consult your healthcare provider if you develop a fever or any discomfort, especially if you live in tick-prone areas.
2. Is vaccination available for Babesiosis?
Currently, there is no vaccine available against human babesiosis.
3. How does Nitric Oxide boost your immune system function?
Here are the far-reaching effects of Nitric Oxide on your immune system.
- Essential for regulating immune responses as a signaling molecule.
- Aids in the activation of other immune cells, improving overall immune response.
- Directly attacks and damages the DNA, proteins, and cell membranes of pathogens, leading to their death.
- Maintains a balance in the synthesis of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines, preventing excessive tissue damage.
- Helps in the communication between the immune cells.
- Promotes vasodilation (widening of blood vessels) and improves blood circulation to the infected regions to efficiently deliver oxygen and immune cells to these sites.
- Inhibits cancer cell growth and enhances natural killer cell activity.
4. Is Babesia infection similar to Lyme disease?
Here is a comparison table:
| Aspect | Babesia Infection | Lyme Disease |
|---|---|---|
| Cause | Caused by the protozoan parasite Babesia | Caused by Borrelia bacteria |
| Transmission | Through tick-bites (black-legged ticks) |
Through tick-bites (black-legged ticks) |
| Symptoms |
Generally asymptomatic Flu-like symptoms: fever, chills, body ache, headache, sweats, fatigue, nausea
|
Stage 1 symptoms: Fever, chills, fatigue, headache, muscle and joint pain, and swollen lymph nodes Stage 2 symptoms: Stage 1 symptoms + body rash, neck pain, facial paralysis, arthritis, nerve pain, irregular heartbeat, pain & numbness in hands or feet, dizziness, shortness of breath, painful swelling in eye/eyelid tissues, vision loss |
| Incubation period | Typically 1-4 weeks after infection | Typically 3-30 days after the tick bite |
| Diagnosis | Blood smear, serology, PCR-based tests | Antibody tests, clinical evaluation |
| Treatment |
Asymptomatic patients don’t need treatment For patients with symptoms, treatment options include: |
Antibiotics (doxycycline, amoxicillin, or cefuroxime axetil) |
| Prevention | Avoiding tick-bites, use of insect repellent, tick checks | Avoiding tick-bites, use of insect repellent, tick checks |
| Geographic Range | United States (Upper Midwest and Northeast), Asia and Europe | United States (Upper Midwest and Northeast), Europe, and Canada |