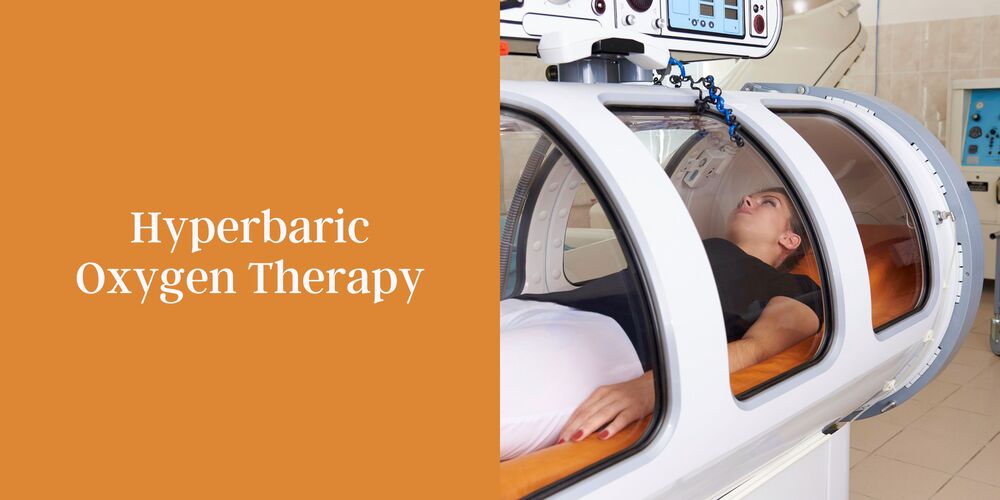
¿Terapia con oxígeno hiperbárico (cámara dura)?
Oxigenoterapia hiperbárica
26 de septiembre de 2023, por Michael Grant White
Conozca más sobre la oxigenoterapia hiperbárica, sus indicaciones, funcionamiento, efectos del aumento de presión y posibles complicaciones del TOHB. Este artículo también analiza los tipos de cámaras hiperbáricas y sus características.

¿Qué es la oxigenoterapia hiperbárica?
La oxigenoterapia hiperbárica (TOHB) es la inhalación intermitente de hasta un 100% de oxígeno a presiones MUCHO mayores que las del nivel del mar. La técnica se puede implementar en una cámara multiplaza (generalmente un gran cilindro de acero) altamente presurizada con aire mientras los pacientes respiran oxígeno al 100%.
Alternativamente, se puede utilizar una cámara monoplaza (para 1 persona), altamente presurizada con oxígeno al 100%. Una variación es la cámara presurizada "suave/blanda", pero es mucho menos efectiva que las cámaras duras.
¿Como funciona?
¿Cuál es el efecto mecánico del aumento de presión?
¿Cuál es el efecto mecánico del aumento de presión?
-
El nitrógeno se disuelve en la sangre. Por lo general, se recomienda a los usuarios médicos hiperbáricos que no viajen en avión durante 24 horas para evitar curvas.
-
Toxicidad pulmonar por oxígeno: 0,00%
Indicaciones de uso
Coronavirus - Tratamiento Hiperbárico
Cámaras duras de oxígeno hiperbárico

Cámaras hiperbáricas suaves (cámaras blandas)
Preguntas más frecuentes
Puedo tener claustrofobia, ¿qué modelo debo elegir?
Un modelo/tamaño grande es el modelo más popular porque proporciona el mayor nivel de espacio y comodidad, así como temperatura, para quienes necesitan espacio. El usuario también puede introducir cualquier dispositivo electrónico portátil dentro de la cámara porque es muy seguro.
¿Qué tipo de % de Oxígeno aporta?
El compresor que viene con la cámara toma aire de la habitación, lo filtra hasta 0,01 micrones y luego lo comprime antes de ingresar a la cámara. Por lo tanto, según la presión que proporciona la cámara, que es 1,3 ATA x 21 % de aire ambiente = 27,3 % (dentro de la cámara)
¿Cómo obtengo más oxígeno si lo necesito?
Si el médico recomienda una fuente adicional de oxígeno según la indicación/aplicación para la que está usando la cámara, se puede usar un concentrador de oxígeno compatible con la cámara haciendo que el paciente use una máscara/cánula dentro de la cámara.
¿Qué tan portátil es una cámara portátil?
Uno de los modelos/tamaños, es lo suficientemente portátil como para poder viajar con él. No es necesario llevar algunas piezas durante el viaje (es decir, estructuras, colchones y cojines); los productos pueden variar según el fabricante.
¿Qué tipo de programas están disponibles?
Hay alquileres mensuales (alquiler con opción a compra) en modelos seleccionados disponibles y/o simplemente comprar la cámara directamente. (Los programas pueden variar dentro de las empresas).
¿Cómo sé qué empresa elegir?
Investigue cuidadosamente la ubicación y las instalaciones, así como su experiencia en la fabricación de estas cámaras, y haga tantas preguntas como pueda imaginar. Echa un vistazo a Evolution Hyperbarics
¿Hay unidades usadas/reacondicionadas disponibles?
¡Ciertamente! Si no hay preferencia por una cámara nueva/usada, nuestra empresa puede tenerlas según disponibilidad, y el precio variará dependiendo de la antigüedad de la cámara. Mi experiencia e investigación me han convencido de que si usted puede hacer ejercicio, el enfoque de ejercicio mejorado con TURBO OXYGEN le brindará beneficios mucho mejores con un costo mucho menor.
La forma más fácil de pensar en el oxígeno hiperbárico versus el ejercicio con el Turbo Oxygen System es que el ejercicio con oxígeno cumple el mismo propósito de empujar oxígeno hacia las células que las cámaras; sólo que es muy superior si puedes hacer ejercicio.
Si puede hacer ejercicio, el ejercicio es muy superior a estar acostado o simplemente sentado, charlando, mirando televisión o frente a la computadora.
Lectura relacionada:
Aprenda a respirar mejor con el kit de dominio de la respiración óptima.

Conoce a Mike White
Conozca a Michael Grant White, el entrenador de respiración óptima y obtenga información práctica sobre el desarrollo de su respiración, su salud y su longevidad.